Your cart is currently empty!
Role of a Purchase Order PO in the Procurement Cycle in Thailand
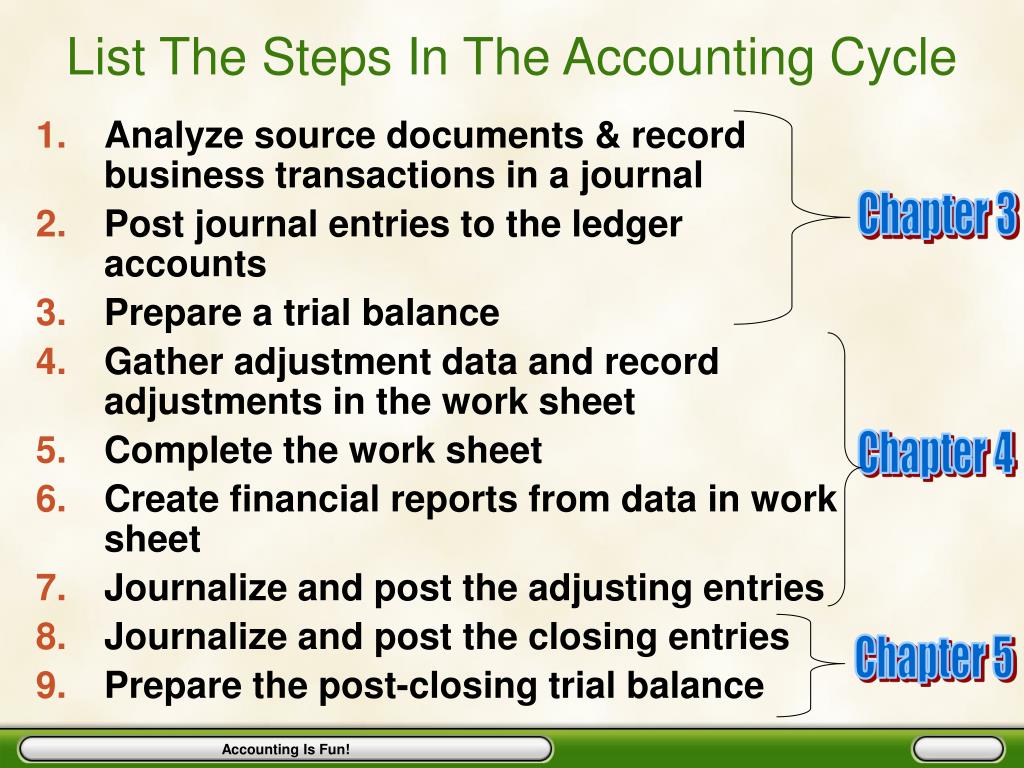
Closing accounts is the last step, where you have to close all temporary accounts such as expenses and revenues (mostly income statement items) to retained earnings and owner’s equity account. This is very essential step to restarting your accounting cycle for the next accounting period. The accounting cycle is a comprehensive accounting process that begins and ends in an accounting period. It involves eight steps that ensure the proper recording and reporting of financial transactions. Once a company’s books are closed and the accounting cycle for a period ends, it begins anew with the next accounting period and financial transactions.
- By following the steps involved in the cycle, businesses can ensure the reliability of their financial statements and make well-informed decisions for their future growth.
- The debits and credits from each journal entry ultimately combine within the general ledger, providing an overview of all financial transactions in the company.
- This allows a bookkeeper to monitor financial positions and statuses by account.
- This section focuses on the process of preparing final statements, including Income Statement and Retained Earnings, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flows.
Company
A trial balance helps check the arithmetical accuracy of recorded transactions. The trial balance is essentially a list of accounts along with their debit and credit amounts. When you record transactions in the journal depends on whether you use cash or accrual exporting invoices in bulk to xero accounting. If you use accrual accounting, you’ll need to match revenue and expenses. The first step in the accounting cycle is identifying business transactions. Companies use internal controls to ensure all transactions are identified and recorded accurately.
Role of a Purchase Order (PO) in the Procurement Cycle in Thailand
The closing statements provide a report for analysis of performance over the period. When a bookkeeper identifies adjustments that need to be made, they have to create new journal entries. These journal entries have to be made in reference to the original transactions. They shouldn’t be done in bulk, and any adjusting entry needs an original transaction for reference. An example of identifying transactions would start with point-of-sale software.
Small Business Resources
In a journal, the transactions are entered in a chronological order, i.e., as and when they happen in business. For example, when a transaction is recorded using accrual accounting, it happens at the time of the sale. This happens regardless of whether or not cash has moved in or out of business. It creates a debit for where the money is going, and a credit for where it is ending up. There are several different amounts of time that a company may choose to report on.
Closing the books
Meanwhile, single-entry accounting is more like managing a checkbook. It doesn’t require multiple entries but instead gives a balance report. The accounting cycle is a comprehensive process designed to make a company’s financial responsibilities easier for its owner, accountant or bookkeeper to manage. The accounting cycle breaks down financial management responsibilities into eight essential steps to identify, analyze and record financial information. It serves as a clear guideline for completing bookkeeping tasks accurately. The seventh step requires to prepare financial statements including the income statement, balance sheet, Statement of Retained Earnings, and cash flow statement.
Step 1: Purchase Request and Order Placing

Without accounting, the financial position of a business cannot be analyzed. Nowadays, most accounting is done through accounting software, making the process much easier. Closing the books takes place at the end of business operations on the last day of the accounting period. Then, the next day, a new accounting period begins, and new books are opened. The accounting cycle is a circular process, and as long as a company is in business it will be active.
Always watch for the separation of personal and business transactions. HighRadius’s solutions not only optimize the accounting cycle but also ensure a faster, error-free close. At the core of HighRadius’s R2R solution lies an AI-powered platform catering to diverse accounting roles. An outstanding feature is its ability to automate nearly 50% of manual repetitive tasks, achieved through a No Code platform, LiveCube. This innovative tool replaces Excel, automating data fetching, modeling, analysis, and journal entry proposals.
Many companies like to analyze their financial performance every month while others focus on quarterly or annual reports. One of the accounting cycle’s main objectives is to ensure all the finances during the accounting period are recorded and reflected in the statements accurately. After adjustments, there is a need to prepare a trial balance again that ensures that all credits and debits are equal. When you record all transactions in the general journal, now, is the time to post these all transactions in the appropriate T account (General Ledger). The Balance Sheet presents the company’s financial position, displaying assets, liabilities, and equity at the end of an accounting period. Assets must equal the sum of liabilities and stockholders’ equity, maintaining the accounting equation.
There are two options; single-entry accounting and double-entry accounting. Single-entry accounting is simple and goes hand-in-hand with cash-basis accounting. It only records a single entry for each transaction, like a chequebook. A business can conduct the accounting cycle monthly, quarterly or annually, depending on how often the company needs financial reports. After analyzing transactions, now is the time to record these transactions in the general journal.
Αφήστε μια απάντηση